The POTS Treatment Center offers a comprehensive, collaborative program aimed at treating the whole person, not just the disorder. Our team consists of a psychophysiologist, an internal medicine doctor, clinical health psychologist, and a registered dietitian who work with you to provide compassionate care through a full range of services. We want patients to leave our program able to live longer, healthier, more enriched lives.
 What is POTS?
What is POTS?
Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome (POTS) is not a specific disease but a syndrome which is a collection of symptoms. It is clinically defined as a heart rate increase of 30 beats per minute or more from the lying down to the standing position within 10 minutes or less. The diagnosis for POTS is usually established when a patient fails the Tilt Table Test: patients usually experience extremely rapid heart rate increase (Tachycardia) over 100 bpm and/or have significant changes in blood pressure. Some patients pass out (syncope). The reason for this problem is a dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system (dysautonomia).
POTS symptoms are widespread and can vary from day-to-day, because the autonomic nervous system plays an extensive role in regulating functions throughout the body.
Causes of POTS
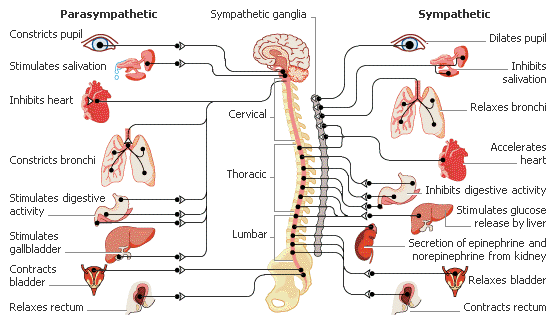
POTS Syndrome may be caused by a variety of factors such as: bacterial infections, injuries, viral infections, surgeries, chemicals, vaccines, severe stress, past traumatic events over challenging the nervous system, and multitasking in overachieving. It may be one or a combination of these factors that can create a perfect storm to activate the Sympathetic Nervous System and start the stress response in an effort to defend and protect. This is the fight-or-flight mode that can eventually lead to a cascade of symptoms.
When the Sympathetic stays in overdrive for too long it triggers a collection of many symptoms resulting in POTS and dysregulation of the Autonomic Nervous System. Therefore, this is a syndrome which is defined as a collection of symptoms.
Common Symptoms of POTS
|
|
|
 The POTS Treatment Program
The POTS Treatment Program
The goal of this program is to gain control of the autonomic nervous system (ANS) and thereby directly addressing the dysautonomia.
When a person has dysautonomia, symptoms are caused by an overactive sympathetic nervous system (they are stuck in “fight or flight” mode). This program engages the parasympathetic nervous system (the relaxation response) which promotes greater balance within the ANS and lessens symptoms. This is done without medication and is therefore more appropriate for these patients, since they tend to have difficulties with taking medication. Patients are eventually able to re-establish an automatic thermostat within their body that controls their bodily functions. To learn more about POTS/Dysautonomia and how it affects the Autonomic Nervous System, click here: The Root of The Problem.
Program Procedures:
- Evaluation
- Daily Consultation
- Autonomic Balance Training
- Education and Group Support
- Nutrition
- Sleep Optimization
- Physiological Stress Management
- Orthostatic Intolerance Training
- Coping Skills
- Lifestyle Management
- SNS Relaxation Training
- Counseling
- Exercise Protocol
- Longterm Progress Monitoring
The POTS Treatment Program™
Patients meet with specialists live online for interactive sessions of the intensive program. The goal of the program is to regulate the Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) and thereby directly address the root cause of the problem.
